The functioning of the endocrine system: glands and hormones
May 11, 2023
This paper discusses the role of the endocrine system in regulating bodily functions and maintaining homeostasis.
The endocrine system is composed of various glands, which produce hormones that are released into the bloodstream to regulate different processes throughout the body. These hormones act on target cells and organs, where they bind to receptors and activate or inhibit specific metabolic pathways. The endocrine system works together with other systems in the body to help maintain balance and ensure proper functioning.
The pituitary gland is the most important endocrine organ, as it controls and regulates the activity of other endocrine glands. The hypothalamus releases hormones that tell the pituitary gland to produce certain hormones, which in turn act on different organs and tissues. For example, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the pituitary gland stimulates the release of thyroxine from the thyroid gland. This thyroxine then binds to receptors on cells throughout the body and helps regulate metabolic rate, energy production, and growth.
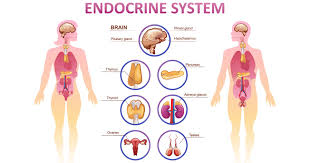
In addition to controlling metabolic processes, hormones released by the endocrine system can affect behavior, moods, development, reproduction, sexual characteristics and appetite. Hormones such as cortisol are released in response to stress and anxiety, while oxytocin is released during childbirth and breastfeeding. Estrogen and testosterone are important hormones that control sexual characteristics, fertility, and reproductive functions.
In conclusion, the endocrine system works together with other systems of the body to maintain homeostasis and regulate many essential processes. The release of hormones by different endocrine glands helps ensure proper functioning of organs throughout the body as well as psychological and physical development. Thus, it is clear that the endocrine system plays a major role in maintaining health and wellbeing.
