The connection between vitamin D deficiency and diabetes mellitus type II.
Apr 06, 2023
This essay discusses the correlation between vitamin D deficiency and diabetes mellitus type II. Diabetes is a long-term, chronic condition in which the body does not produce enough insulin or cannot effectively use the insulin that it produces. This results in elevated blood glucose levels, which can lead to complications such as kidney damage, heart disease and stroke if left untreated.
Diabetes Mellitus type II is associated with an increased risk of vitamin D deficiency. Vitamin D helps to regulate glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, which are important for people with diabetes. Low levels of vitamin D can cause impaired insulin secretion and may contribute to the development of type II diabetes.
In clinical studies, a correlation has been observed between low levels of vitamin D in people with type II diabetes and increased severity of their symptoms. A study conducted by the National Institutes of Health found that adults with low levels of vitamin D had an increased risk for developing type II diabetes compared to those with higher levels. The study also showed that adults who supplemented their diets with vitamin D supplements experienced lower risks for developing type II diabetes than those who did not take any supplementation.
Vitamin D plays an important role in regulating blood sugar levels, reducing inflammation and promoting bone health. Studies have shown that people who are deficient in vitamin D are more likely to develop diabetes mellitus type II than those with normal vitamin D levels. Low levels of vitamin D have been linked to increased insulin resistance, decreased pancreatic beta cell function and reduced adiponectin levels—all factors that contribute to the development of diabetes.
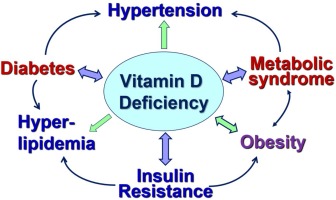
Additionally, a lack of vitamin D can lead to decreased physical activity, further increasing the risk for diabetes. It is important for those at risk for developing diabetes to get their vitamin D levels tested and supplement if necessary in order to reduce their risk of developing type II diabetes. In conclusion, while there is no clear cause-and-effect relationship between vitamin D deficiency and diabetes mellitus type II, it has been strongly linked and should be taken into account when considering potential causes of the disease. Thus, it is important that individuals at risk take steps to ensure they are getting enough vitamin D in order to reduce their chance of developing this serious condition.
